Overview
This article guides you on how to set up Wake-on-LAN on a Windows operating system for the GFI LanGuard to wake up the target machines.
Prerequisites
The motherboard and the network interface card of the computer running GFI LanGuard must support Wake-on-LAN.
Solution
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or woken up by a network message. WoL enables GFI LanGuard to wake machines from the following states:
- Powered off
- Sleep
- Hibernated
This is done by the GFI LanGuard sending a message to the same local area network or to another network by using Subnet directed broadcasts.
IMPORTANT: If you have routers between the client machine and the GFI LanGuard server, the router and the GFI LanGuard server must be configured to allow Wake-on-LAN broadcast packets on UDP port 9.
To configure Wake-on-LAN on a Windows operating system:
- Run Device Manager by opening the Run dialog box with Windows+R keys, typing devmgmt.msc, and pressing Enter.
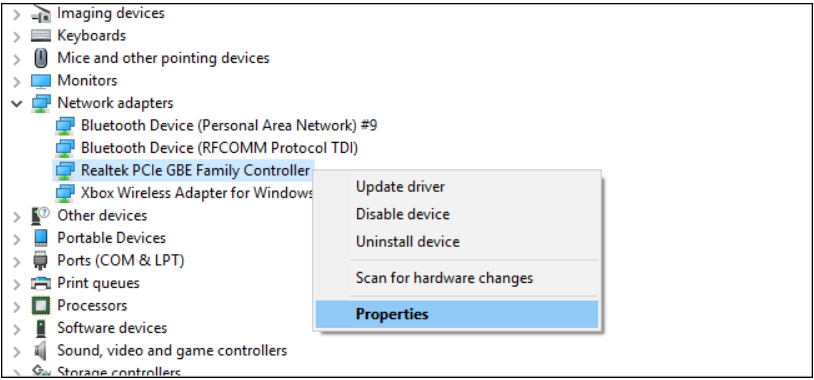
- Expand the Network Adapters section. Right-click on your network card and go to Properties. select Properties.
- From the Power Management tab, select the following options:
- Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.
- Allow this device to wake up the computer
- Only allow a magic packet to wake the computer
NOTE: Magic Packet is the wake-up signal that is sent by GFI LanGuard to the scan target network card.
-
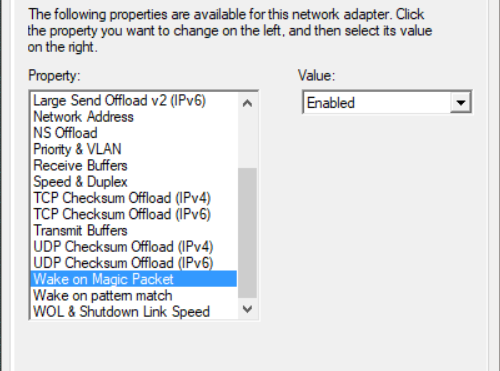
For some network cards, it may be necessary to configure additional settings in the Advanced tab. For example:
NOTE: refer to your network card provider technical manual and support for more information. card.
- Click OK.
Once the Network Interface Card is configured, run a FULL scan on the client machine, refer to Performing a Manual Scan if necessary. This enables GFI LanGuard to gather the required information from the client machine.

Priyanka Bhotika
Comments